Login
Notebooks
Categories

Cells

Required GPU
In order to run this notebook, GPU resources are required.
Required PFP
You can run external processes, such as Shiny apps, alongside your
notebook using this feature.
Notebook
Premium

BioTuring
In the realm of cancer research, grasping the intricacies of intratumor heterogeneity and its interplay with the immune system is paramount for deciphering treatment resistance and tumor progression. While single-cell RNA sequencing unveils diverse transcriptional programs, the challenge persists in automatically discerning malignant cells from non-malignant ones within complex datasets featuring varying coverage depths. Thus, there arises a compelling need for an automated solution to this classification conundrum.
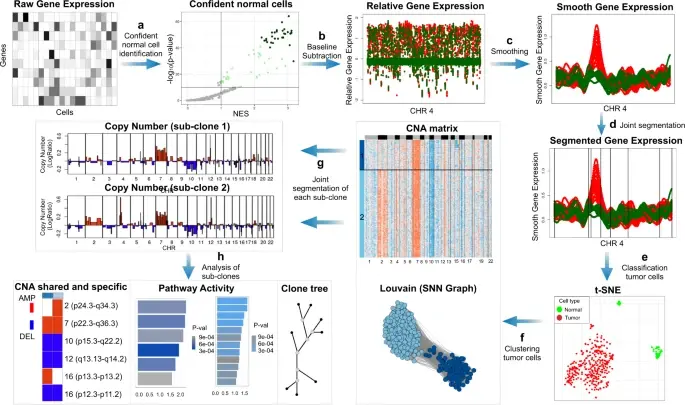
SCEVAN (De Falco et al., 2023), a variational algorithm, is designed to autonomously identify the clonal copy number substructure of tumors using single-cell data. It automatically separates malignant cells from non-malignant ones, and subsequently, groups of malignant cells are examined through an optimization-driven joint segmentation process.
Required GPU
scevan

BioTuring
Computational methods that model how the gene expression of a cell is influenced by interacting cells are lacking.
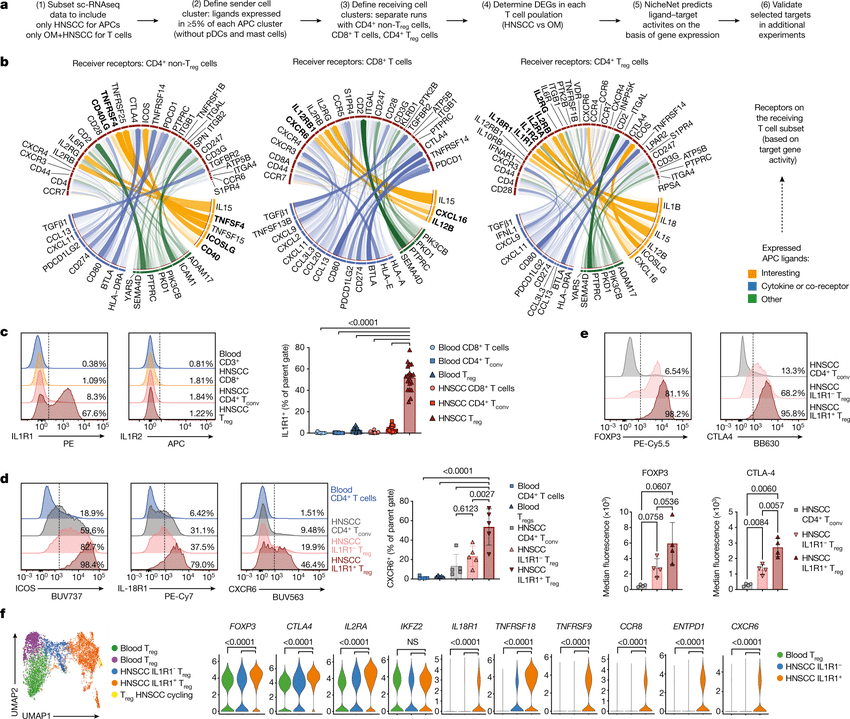
We present NicheNet, a method that predicts ligand–target links between interacting cells by combining their expression data with prior knowledge of signaling and gene regulatory networks.
We applied NicheNet to the tumor and immune cell microenvironment data and demonstrated that NicheNet can infer active ligands and their gene regulatory effects on interacting cells.
Only CPU
nichenetr

BioTuring
The development of immune checkpoint-based immunotherapies has been a major advancement in the treatment of cancer, with a subset of patients exhibiting durable clinical responses. A predictive biomarker for immunotherapy response is the pre-existing T-cell infiltration in the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME).
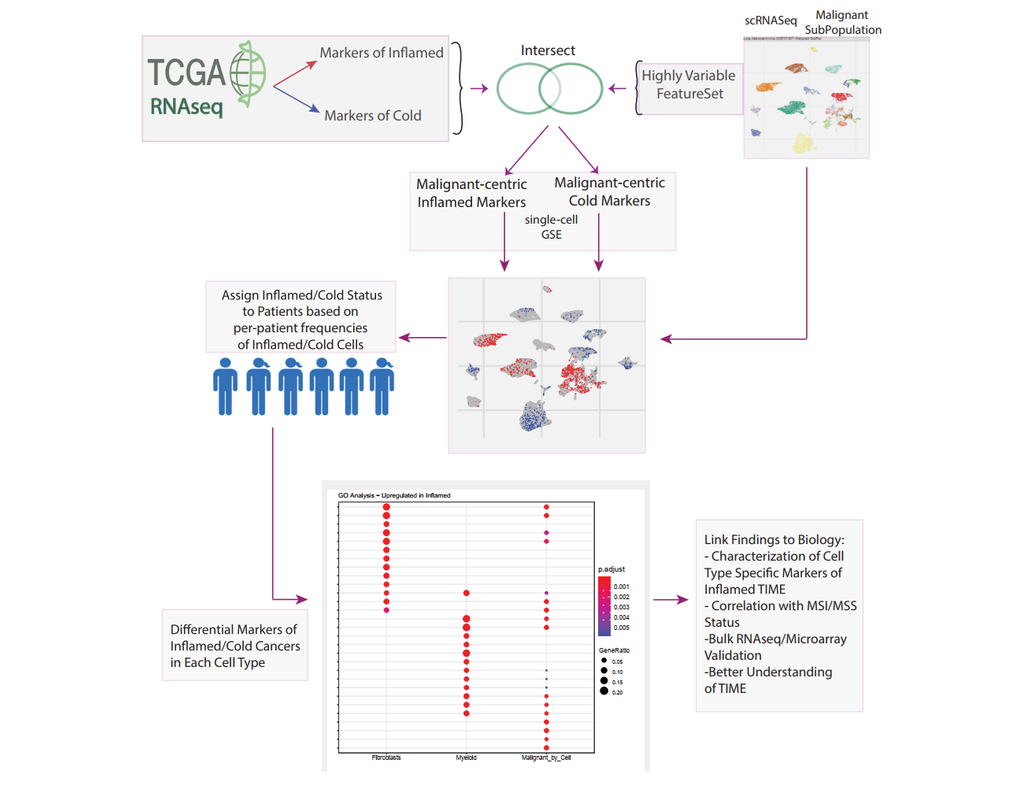
Bulk transcriptomics-based approaches can quantify the degree of T-cell infiltration using deconvolution methods and identify additional markers of inflamed/cold cancers at the bulk level. However, bulk techniques are unable to identify biomarkers of individual cell types. Although single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNAseq) assays are now being used to profile the TIME, to our knowledge there is no method of identifying patients with a T-cell inflamed TIME from scRNAseq data. Here, we describe a method, iBRIDGE, which integrates reference bulk RNAseq data with the malignant subset of scRNAseq datasets to identify patients with a T-cell inflamed TIME.
Utilizing two datasets with matched bulk data, we show iBRIDGE results correlated highly with bulk assessments (0.85 and 0.9 correlation coefficients). Using iBRIDGE, we identified markers of inflamed phenotypes in malignant cells, myeloid cells, and fibroblasts, establishing type I and type II interferon pathways as dominant signals, especially in malignant and myeloid cells, and finding the TGFβ-driven mesenchymal phenotype not only in fibroblasts but also in malignant cells.
Besides relative classification, per-patient average iBRIDGE scores and independent RNAScope quantifications were utilized for threshold-based absolute classification. Moreover, iBRIDGE can be applied to in vitro grown cancer cell lines and can identify the cell lines that are adapted from inflamed/cold patient tumors.
Only CPU
iBRIDGE

BioTuring
Charting an organs’ biological atlas requires us to spatially resolve the entire single-cell transcriptome, and to relate such cellular features to the anatomical scale. Single-cell and single-nucleus RNA-seq (sc/snRNA-seq) can profile cells comprehensively, but lose spatial information.
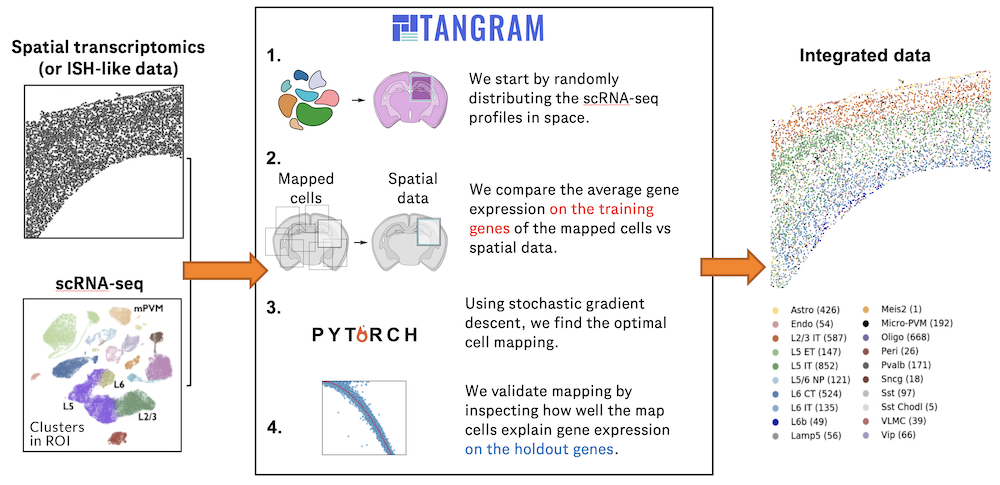
Spatial transcriptomics allows for spatial measurements, but at lower resolution and with limited sensitivity. Targeted in situ technologies solve both issues, but are limited in gene throughput. To overcome these limitations we present Tangram, a method that aligns sc/snRNA-seq data to various forms of spatial data collected from the same region, including MERFISH, STARmap, smFISH, Spatial Transcriptomics (Visium) and histological images.
**Tangram** can map any type of sc/snRNA-seq data, including multimodal data such as those from SHARE-seq, which we used to reveal spatial patterns of chromatin accessibility. We demonstrate Tangram on healthy mouse brain tissue, by reconstructing a genome-wide anatomically integrated spatial map at single-cell resolution of the visual and somatomotor areas.
Required GPU
Tangram


